Let's look at what a herniated disc is, what causes it, and what methods of diagnosis and treatment are available. Finally, we will try to answer the most important question: Can a herniated disc be repaired without surgery?
What is spinal disc herniation
The vertebral column supports the balance of the trunk when walking, so it must be strong, but also flexible and agile. There are 24 vertebral segments that are responsible for the movement of the spine, with 23 cartilage layers between them, they are the intervertebral discs. An intervertebral disc is a kind of safety cushion for the vertebrae. It helps to closely connect the vertebrae to each other to ensure their mobility and cushioning (to soft shocks and damp vibrations). The intervertebral disc can be thought of as a flat capsule with a gel-like content.
It consists of several elements
- A jelly-like nucleus pulposus is made up of glycosaminoglycans (capable of attracting water molecules). It is responsible for shock absorption.
- The fibrous ring around the nucleus pulposus holds the gel-like matter inside and fuses tightly to the adjacent vertebrae.
- Hyaline cartilage plates cover the disc from above and below, participate in the transport of water, nutrients and excretion of metabolic products.
- Laminae are rigidly connected to the bodies of adjacent vertebrae.
When a person lifts weights, the nucleus pulposus absorbs water and expands, thereby compensating for the load and protecting the vertebrae. When a person walks, water is pushed out of the nucleus and the nucleus flattens out. But for a number of reasons, the fibrous ring around the nucleus can break down: become fibrous, loose, with gaps and tears in the structure. In this case, the content of the nucleus shifts outside the intervertebral disc. This is how a hernia occurs.
A disc herniation is a bulging of the nucleus pulposus outside the intervertebral disc space. It occurs when the fibrous ring around the nucleus breaks down.
The body is an integral system, nothing happens by itself. Intervertebral hernia occurs for a number of serious reasons:
- Lack of nutrients supplied to the disc tissue (dystrophy). Since the disc is nourished by nutrients that diffuse through it, human physical activity plays an important role in this process. The lack of physical activity can damage the disc.
- Congenital disorder of the disc (dysplasia).
- Trauma consequences.
- Age-related degeneration (aging).
- Muscular imbalance.
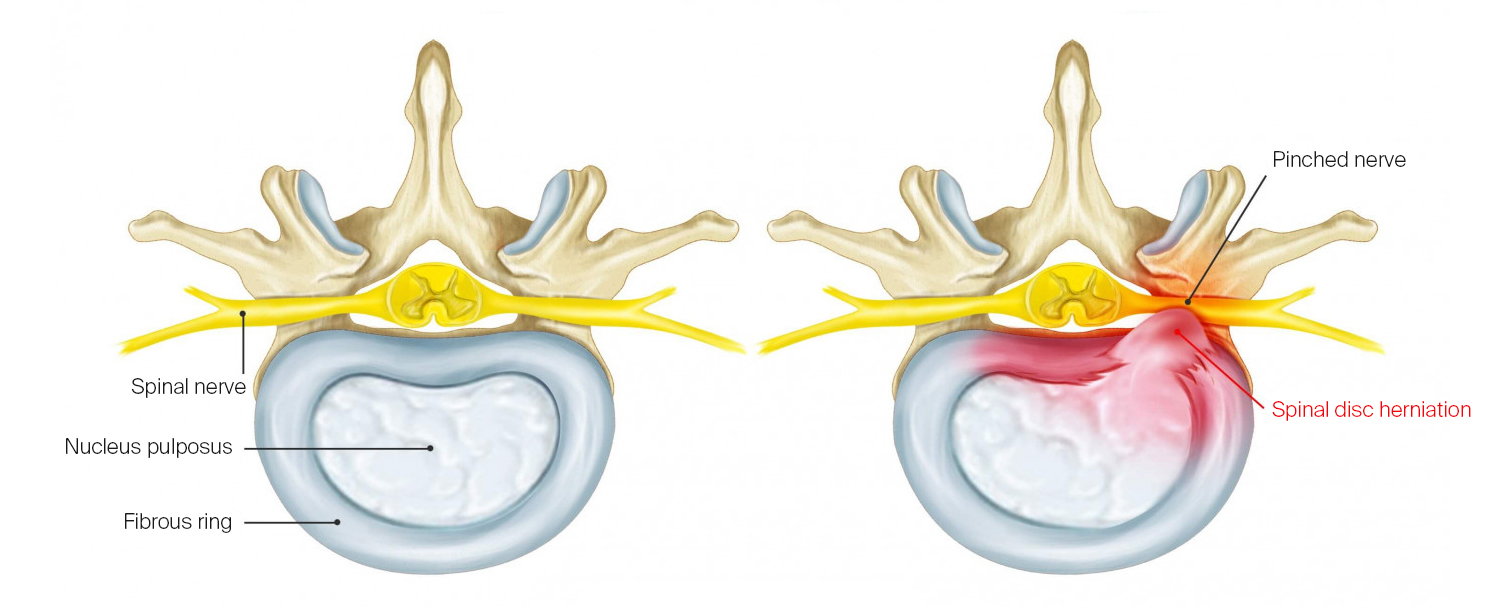
Normal intervertebral disc and herniated disc
Symptoms of spinal disc herniation
The main symptom of a spinal disc herniation is back pain. The doctor takes into account the localization and distribution of pain when making a diagnosis and choosing the optimal treatment, so it is highly discouraged to uncontrollably relieve pain with pain medications. Pain may be caused by:
1. Prolonged pressure (compression) on the roots of spinal nerves. The medical term for this syndrome is radicular syndrome (radiculopathy).
2. Inflammatory process and soft tissue swelling.
3. Myofascial pain syndrome caused by muscular imbalance as a result of a long-term illness.
Patients with disc herniation do not always suffer pain. During the initial stage of the disease there may be no pain. It is explained by the fact that cartilage, bone tissue and nerve fibers do not have their own pain receptors.
In addition to back pain, a herniated spinal disc can cause:
- reduced skin sensation;
- muscle weakness;
- pelvic organ dysfunction – herniated lumbar disc;
- Dizziness - herniated cervical disc.
A rarer but the most dangerous group of symptoms is cauda equina syndrome, damaged bundle of nerves below the end of the spinal cord. It is characterized by all the above symptoms, as well as numbness and impaired sensitivity in the lower limbs and crotch (the tight pants syndrome). This is an indication for urgent neurosurgical treatment.
The classification of intervertebral disc herniation is based on the anatomical location. Abbreviated Latin names of the vertebral column regions and the ordinal number of the vertebra in that region are used:
1.Cervical region (Pars cervicalis): vertebrae CI - CVII. The most frequent cause of pain in the neck, shoulders, upper extremities.
2.Thoracic region (Pars thoracalis): vertebrae TI - TXII. Disc herniation are rarely localized in this region because of decreased thoracic mobility, and therefore less wear and tear of the intervertebral discs.
3.The lumbar region (Pars lumbalis): vertebrae LI - LV. Lumbar have the greatest load to bear, and it is not only overall vertical load but also oblique load. Herniated discs occur more commonly in this segment.
4. The sacrum (Os sacrum): vertebrae SI - SV. Hernias at the border of the lumbar and sacral region are the most common.
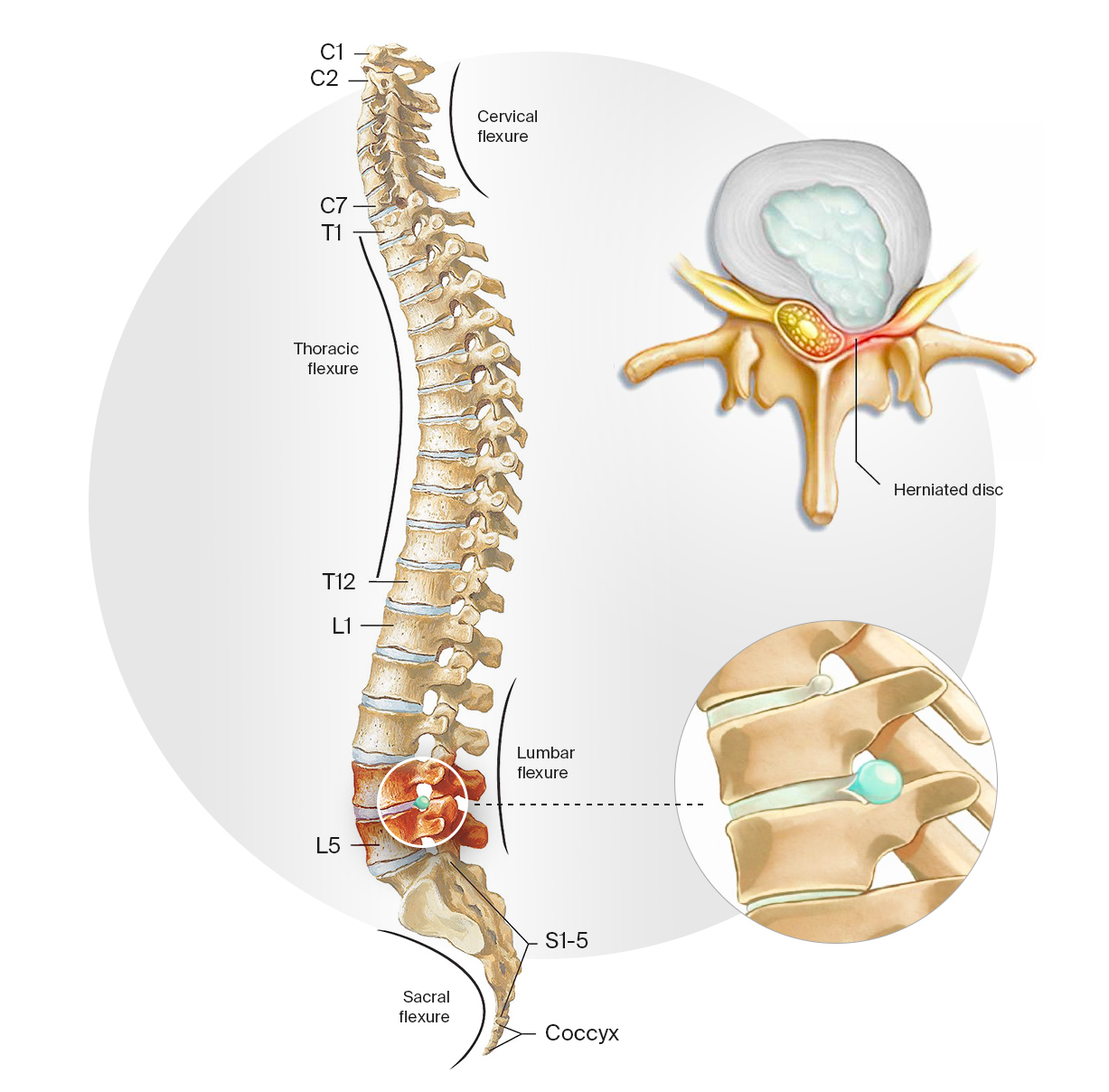
Localization of disc herniation. They most commonly occur in vertebrae LI to LV
Disc herniation diagnostic methods
Two main methods are used to visualize abnormal tissues in the case with disc herniation - computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Computed tomography (CT). This method also uses the principle of X-rays, but with computer processing. You can get a series of longitudinal and cross-sectional scans that show details of bone and cartilage tissue. Nerve fibers and soft tissue cannot be seen.
Myelography. A contrast agent is injected into the spinal canal to increase the informative value of the CT scan. It allows to see on the slices details that cannot be seen on a standard CT scan.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Today it is the gold standard for the diagnosing pathologies, including soft tissue pathology.
Contrast discography. Compared to myelography a contrast agent is injected directly into the intervertebral disc.
Electroneuromyography. This functional examination may be prescribed as an additional test to measure impulse conduction along nerve fibers.
All diagnostic methods are of no value without examination by a specialist. Not only the scan is important, but also the interview with the patient because a herniated disc can be of considerable size, but a patient may not feel any discomfort. Or, alternately, a very small herniated disc may cause severe pain syndrome.
Doctors at the Tkachev & Epifanov Clinic conduct in-person and online consultations. They examine MRI scans and interview a patient. The preliminary consultation is free of charge.

Non-surgical treatment option for disc herniation
Treatment of a herniated disc is a complicated and long process. Pathology has been developing for a long time and it is impossible to reverse during one visit to a doctor. Essentially, there are only to treatment options for a herniated disc: non-operative and surgical. What about a non-operative option? Specialists have observed that in a large number of cases disc herniation reduces over time until it completely disappears. This process is called spontaneous resorption, that is, the resorption of disc herniation.
It is inflammation that causes hernia resorption. Macrophages, immune blood cells, engulf the affected areas of the intervertebral disc and then proceed to eliminate the inflammation. The resorption process is not yet fully understood. But doctors know how to create favorable conditions for the spinal disc tissue to regenerate itself. This allows to treat a herniated disc without surgery.
Resorption is the natural reduction of disc herniation which occurs due to the inflammatory process. One way to trigger resorption is the Tkachev & Epifanov method.

The usual complex of conservative treatment is aimed at relieving pain and triggering hernia resorption. This complex includes several approaches and techniques. Medications are prescribed to control pain syndrome, relieve edema (nonsteroidal and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), and relax muscles (muscle relaxants).
Physiotherapy is a general term. Treatment is based on natural and artificial physical factors (cold, heat, electric current, magnetic radiation, laser, etc.). This treatment is performed by various medical specialists: chiropractor, osteopath, massage therapist, acupuncturist, physical therapy instructor, etc. Physiotherapy may involve the use of special apparatuses, devices and manual techniques.
Kinesiotherapy (movement therapy): active (physical therapy) and passive (massage, traction). Movement therapy is tailored to the individual patient and is aimed to strengthen the back muscles. Traction helps to relieve pain and muscle tension.
Chiropractic care and massage are methods of working upon soft tissues and joints to restore balance to the body and synchronize processes. These methods restore mobility and eliminate pain.
Taping, kinesiology taping is a method of placing special patches on the skin to affect muscle receptors through stretching and compression. A way of relaxing or strengthening the tone of the muscles.
Laser therapy (light therapy) is based on biological activation of regeneration processes.
Plasma therapy (prp-therapy) uses injections of a patient’s own purified plasma rich in platelets, growth factors, and hormones to increase local immunity and trigger regeneration processes.
Reflexology, acupuncture (treatment with biological energy) is the stimulation of nerve endings using special needles. In this way microdoses of medications can be administered. The metabolism of the affected areas is improved and pain is relieved.
Shockwave therapy uses extremely high-frequency waves that causes resonance. It allows to initiate self-healing processes.
Orthopedic devices are also used: insoles, orthoses. They can partially compensate for the load on the spine.
Non-surgical treatment for disc herniation
Surgery compared to non-surgical methods is a relatively short treatment route, but it is not indicated for everyone. After surgery, complications and relapses are possible, and rehabilitation includes conservative therapy methods and may take an indefinite period of time. Absolute indications for neurosurgical intervention are necessary, i.e. critical life-threatening disorders. Absolute indications for surgical treatment for disc herniation are:
- cauda equina syndrome and movement disorders;
- progressive neurological symptoms and conservative treatment lumbar disc herniation for 1-2 months, which did not help the patient;
- recurrence of acute pain after surgery.
Tkachev & Epifanov Clinic offers individualized treatment
In any treatment, a medical specialist is of fundamental importance. Their experience and intuition are critical because every case is different; treatment options for one patient may not suit and even harm another. One of the clinics where doctors with extensive experience in the treatment of intervertebral hernias offer their help is the Tkachev-Epifanov Clinic. The clinic uses a unique method for treating disc herniation. This is a complex course which stimulates hernia resorption and, consequently, leads to complete freedom from pain and discomfort. The clinic has helped more than 1200 patients. More about the results you can read in sections Clinical Cases and Patient Reviews. Here is a feedback from Kuzmenko Philip, a general practitioner who runs popular health groups on social networks.
“If there are any health problems, I recommend going to Tkachev & Epifanov Clinic. Their approaches are provably effective and approved.They will fight for the health of your back to the last minute. I highly recommend”
Kuzmenko Philip @dr.philipp
Doctors at Tkachev & Epifanov Clinic offer free preliminary consultations. They evaluate the condition of the spine using MRI scans, report on the likelihood of resorption and offer treatment options. Preliminary prognosis can be obtained online.

